Organizational Culture: What It Means and How to Strengthen It
Organizational culture encompasses the collective values, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors that affect how individuals within a company collaborate and operate. It defines a business’s overall personality, influencing everything from decision-making to how staff treat each other and customers.
The following resource provides business leaders with a comprehensive guide to understanding organizational culture (also known as company or workplace culture), highlighting its importance, common types, key characteristics of success, and strategies for improvement and measurement.
What is organizational culture?
Organizational culture is the shared values, beliefs, behaviors, and norms that shape how employees interact, make decisions, and approach their work. It’s essentially a business’s personality and reflects its priorities, leadership style, and workplace practices.
Workplace culture isn’t just about what’s written in the company handbook; it’s how things actually get done and how staff experience their daily responsibilities. A positive culture is a competitive advantage, while a negative one can lead to poor morale and high turnover.
Why is organizational culture important?
An organization’s culture impacts its every function. It affects outcomes both within and outside the business, from productivity and employee retention to customer experience and brand reputation.
Employee engagement and retention
A company’s culture greatly influences staff’s engagement and long-term retention. Per Gallup, those who feel strongly connected to their organization’s culture are:
- 4x as likely to be engaged at work
- Nearly 6x as likely to agree to recommend their company as a great place to work
- 62% less likely to often or always feel burned out at work
- 43% less likely to be actively or passively seeking another job
This connection pays off—companies with high levels of employee engagement are 23% more profitable than those with low engagement.
Productivity and performance
When employees feel supported and valued within their organization’s culture, they’re more likely to be motivated and give their best effort. In fact, research shows that satisfied employees are 12% more productive than the average worker, leading to greater efficiency, innovation, and overall performance.
Attracting talent
Work Institute’s 2025 Retention Report found that a poor environment is among the top reasons for employees leaving, and nearly 90% of job seekers believe a healthy culture is necessary for success. These figures demonstrate the importance of a strong organizational culture in recruiting top talent.
Brand reputation and customer service
A culture that empowers and engages employees positively impacts the organization’s reputation with its customers, business partners, prospective talent, and the public. When employees are satisfied at work, they bring greater innovation and deliver exceptional customer service. This satisfaction also strengthens the employer brand by driving higher ratings on employer review sites like Glassdoor and Indeed.
Alignment with vision and goals
Clearly outlined core values are a critical part of an effective organizational culture. When employees internalize these principles, they are inspired to reinforce the company’s mission through their actions and decisions, ultimately driving business success.
Types of organizational culture
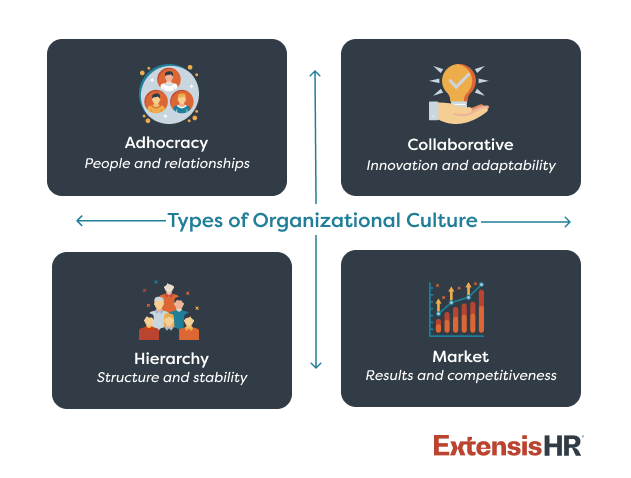
Defining corporate culture can feel challenging, as it is a complex, multifaceted concept shaped by deeply ingrained values, beliefs, and behaviors. However, most organizational cultures fall into one of four major types: adhocracy, collaborative, hierarchy, or market.
| Culture Type | Characteristics | Strengths | Challenges | Example Organizations |
| Adhocracy | Focuses on innovation and adaptability Encourages risk-taking, creativity, and thinking outside the box Leadership encourages experimentation and visionary thinking | Very innovative and adaptable to market changes Excels in industries that value disruption | Can lack structure and lead to employee burnout and inefficiency | Startups, technology companies, design firms |
| Collaborative | Focuses on people and relationships Values teamwork, collaboration, and employee development Leadership acts as mentors | High employee satisfaction and loyalty Strong sense of belonging and community | May struggle with competition and rapid innovation | Small businesses, family-owned companies, organizations with a flat hierarchy |
| Hierarchy | Focuses on structure, stability, and efficiency Emphasizes clear roles, rules, and procedures Leadership ensures processes are followed and goals are met | Predictable, consistent performance Good fit for industries with strict regulations or complex processes | Can be rigid and resistant to change | Government agencies, healthcare institutions, manufacturing companies |
| Market | Focuses on results, goals, and competitiveness Prioritizes customer satisfaction and achieving measurable success Leadership is goal-oriented and demanding | High productivity and profitability Successfully achieves objectives and remains competitive | Can result in a high-pressure environment that neglects employee well-being | Sales-driven companies, businesses in highly competitive industries |
Characteristics of a good workplace culture
Each business, along with its culture, is distinct. However, strong workplace cultures often share several key traits:
Open communication: A corporate culture centered around open communication acts as a catalyst for enhanced employee engagement, higher productivity levels, and increased inclusion.
A focus on employee well-being: Businesses that prioritize employee well-being through comprehensive employee benefits and a fair work-life balance tend to have happier, healthier, and more productive staff.
Influential leadership: Leaders set the tone for how employees interact, work, and perceive the organization. They make a positive impact by establishing and reinforcing the company’s core values, encouraging feedback, involving workers in decision-making, and embracing change.
Shared values and purpose: A business’s core values and purpose are the foundation of its culture, shaping how employees interact, make decisions, and perceive their roles. Core values create a positive and cohesive workplace when well-defined and actively practiced.
Employee recognition: A robust employee recognition program can enhance an organization’s culture by boosting morale, reducing turnover, increasing employee engagement, encouraging collaboration, and more.
Inclusivity: The diverse perspectives found in inclusive work environments can improve employee morale, drive innovation, and enhance decision-making and problem-solving, among other benefits.
Learning and development opportunities: Professional development plays a vital role in shaping a business’s culture. It instills a growth mindset, increases institutional knowledge, and helps the company adapt to industry changes. Additionally, it increases employee retention, as lack of advancement opportunities is the top reason people leave their jobs.
Innovation and agility: Strong organizational cultures hold a forward-thinking mindset, prioritizing continuous improvement, creative thinking, and cross-functional collaboration.
Accountability and fairness: A strong organizational culture involves treating everyone fairly and individuals taking ownership of their actions and fulfilling their commitments. These actions foster trust, transparency, and teamwork.
How to improve workplace culture
Improving workplace culture requires a thoughtful approach, recognizing that it naturally evolves from employee interactions. However, the right company policies can set the stage for success. Here are some actionable steps for employers to consider:
Encourage open communication
Businesses can promote open dialogue and empower staff to use their voices by:
- Creating channels for employees to voice their concerns, ideas, and feedback (i.e., anonymous surveys, one-on-one meetings between managers and direct reports, team meetings, etc.)
- Ensuring transparent communication from leadership about goals, challenges, and successes
Recognize and reward achievements
To boost morale, motivation, and engagement, employers should practice the following:
- Acknowledging individual and team accomplishments through shout-outs, awards, bonuses, etc.
- Celebrating milestones like work anniversaries, achieving certifications, and successful project completions
Prioritize employee well-being
Companies can prevent staff burnout and promote physical and mental health by:
- Offering flexible work schedules, remote work options, and wellness programs
- Providing access to mental health resources or counseling
- Encouraging work-life balance by deterring after-hours emails or excessive overtime
Meaningfully foster inclusion
Every employee should feel a genuine sense of belonging at work. To achieve that, organizations must implement diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives that effectively support their workforce, including:
- Administering diversity and inclusion training
- Building diverse teams and ensuring equal opportunities for growth and leadership roles
- Celebrating various cultural events
- Creating employee resource groups
Build an effective leadership team
A powerful, influential leadership team drives employee trust and engagement, and can be achieved by:
- Training leaders to be empathetic, transparent, and supportive
- Ensuring managers model the behavior and values they expect from their teams
Offer growth opportunities
When employees clearly understand how they can progress within their companies, they feel valued, motivated, and more loyal. To achieve this, business leaders should consider:
- Investing in professional development through training, certifications, and mentorship programs
- Leveraging internal promotions and career pathing
- Organizing cross-departmental projects to expand skillsets
Support collaboration and team-building
The best business outcomes are driven by teamwork. Some proven methods of strengthening relationships and nurturing a sense of community are:
- Hosting team-building activities, social events, and cross-functional projects
- Utilizing collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams or Slack to improve communication
Define, communicate, and embody core values
Core values motivate employees and connect them to the company’s purpose. Best practices for doing so include:
- Clearly articulating the organization’s mission, vision, and values and sharing them broadly (through the employee handbook, company intranet, and office signage)
- Aligning policies and behaviors with these values, demonstrating they’re more than just words
Provide regular feedback
Managers can build trust, engagement, and continual improvement in their teams by:
- Conducting performance reviews focusing on strengths and areas for improvement
- Embracing two-way feedback and allowing workers to share their input on leadership and processes
Promptly address harmful workplace conduct
To create a safe, supportive work environment, business leaders can:
- Set clear expectations for conduct and communicate them via the employee handbook
- Consistently enforce consequences for inappropriate or unprofessional actions
- Promote a culture of respect and zero tolerance for harassment or discrimination
Encourage innovation and creativity
Some strategies to encourage employees to be dynamic and adaptable include:
- Creating safe spaces for brainstorming and experimenting with new ideas
- Rewarding staff who take calculated risks or discover innovative solutions
Measuring organizational culture
Workplace culture naturally develops and evolves over time, but employers can take a hands-on role by tracking its health and using that data to drive improvement.
To measure company culture, business leaders should monitor:
- Turnover: Lower turnover rates signal a positive culture
- Employee feedback: Encourage workers to share their opinions by administering employee pulse surveys and providing an anonymous suggestion box
- Workplace reviews: Read reviews on sites like Glassdoor, Indeed, etc., to better understand the experiences of current and former employees (as well as those who interviewed but did not ultimately work for the company)
Resources and tools
An effective company culture doesn’t happen accidentally; it requires knowledge, the right tools, and a dedication to ongoing improvement. Whether you’re looking for a complete cultural transformation or simply want to stay up to date with the latest trends, the following resources provide valuable guidance.
Industry news and trends
- The Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) – With nearly 340,000 members in 180 countries, SHRM is an HR industry “expert, researcher, advocate, and thought leader on issues and innovations impacting today’s evolving workplaces.”
- Harvard Business Review (HBR) – A general management magazine published by an independent, non-profit affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Korn Ferry – A global organizational consulting firm specializing in executive research, leadership and talent consulting, and workforce management.
Outsourced expertise
- Partnership with a professional employer organization (PEO) – PEOs are a type of human resource outsourcing service that help small- and medium-sized businesses manage various aspects of their HR, recruiting, employee benefits, payroll, risk and compliance, and more.
Tools and technology
- 15Five – An industry-leading performance management software that facilitates public and private recognition and one-on-one meetings where feedback and acknowledgment can be shared.
- ExtensisHR’s DEI Dashboard – An intuitive diversity metrics tool featuring real-time data on pay equity, salary trends across gender and race demographics, employee turnover, promotions, and more.
- Glassdoor and Indeed – Job review websites where employees can share opinions on their workplaces and job seekers can explore information about companies’ cultures, work-life balance, and more.
FAQs for workplace culture
How does workplace culture influence productivity?
According to the Harvard Division of Continuing Education, a poor workplace culture can result in low productivity, while a positive corporate culture leads to higher rates of productivity.
Why is culture important in the workplace?
Workplace culture is important because it shapes the overall environment where employees work, influencing their motivation, performance, and job satisfaction.
A strong, positive culture benefits both staff and the organization by:
• Enhancing employee engagement and satisfaction
• Reducing turnover and helping attract top talent
• Boosting productivity and performance
• Fostering trust, collaboration, and teamwork
• Driving a higher level of customer service
• Encouraging workplace integrity and accountability
How do you improve company culture?
Improving company culture requires intentional efforts to develop a positive, engaging, and inclusive work environment.
Here are some key strategies:
• Encourage open communication
• Recognize employees’ achievements
• Prioritize workforce well-being
• Meaningfully drive inclusion
• Build an influential leadership team
• Offer professional development opportunities
• Organize team-building activities and programs
• Develop, share, and abide by core values
• Provide consistent feedback on performance
• Consistently enforce consequences for unprofessional behavior
• Nurture a mindset that prioritizes innovation and creativity
What are the different types of work cultures?
The four main types of work cultures are:
• Adhocracy: Driven by innovation and adaptability.
• Collaborative: Focused on people and relationships.
• Hierarchy: Prioritizes structure, stability, and efficiency.
• Market: Revolves around results, goals, and competitiveness.



